OceanBase MCP Server
Background information
AI tools are evolving rapidly, from graphical solutions like Cursor, Windsurf, and Trae to command-line options such as Claude Code, Gemini CLI, and Qwen Code. Empowered by Agent-based frameworks, these tools are remarkably capable. However, a key limitation remains: AI tools cannot directly access databases, leaving a gap between data and analysis. The MCP protocol bridges this gap. By leveraging the MCP protocol, OceanBase MCP Server enables AI tools to interact directly with databases and retrieve data seamlessly.
Traditionally, data analysis tasks—such as user analytics, product analysis, order tracking, and user behavior analysis—require developers to build backend systems for data retrieval and frontend interfaces for data visualization. Even with BI tools, some familiarity with SQL is often necessary. While data can be displayed, understanding the underlying logic or making business decisions based on that data still depends on the expertise of data analysts.
The combination of AI tools, MCP, and large language models (LLMs) is transforming the way data analysis is performed. Analysts no longer need to rely on developers or have SQL knowledge. They can simply describe their requirements to AI tools and instantly receive the results they need—complete with attractive charts and initial data insights.
Functional architecture
Core toolkit
OceanBase MCP Server offers standardized interfaces that enable AI tools to interact directly with the database:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
execute_sql | Executes any SQL statement (such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, DDL). |
get_ob_ash_report | Gets seekdb Active Session History (ASH) reports for performance diagnostics. |
get_current_time | Returns the current time of the seekdb instance. |
oceanbase_text_search | Performs full-text searches across seekdb database tables. |
oceanbase_vector_search | Executes vector similarity searches within seekdb database tables. |
oceanbase_hybrid_search | Conducts hybrid searches, combining relational filtering with vector search. |
ob_memory_query | Retrieves historical conversation records from the AI memory system using semantic search. (AI Memory System Tool) |
ob_memory_insert | Automatically captures and stores important conversation content to build a knowledge base. (AI Memory System Tool) |
ob_memory_delete | Deletes outdated or redundant conversation memories. (AI Memory System Tool) |
ob_memory_update | Updates or evolves memory content based on new information. (AI Memory System Tool) |
Resource endpoints
AI tools can directly access these resource endpoints via the MCP protocol:
| Resource path | Description |
|---|---|
oceanbase://tables | Lists all tables in the database. |
oceanbase://sample/{table} | Retrieves sample data (first 100 rows) from the specified table. {table} can be dynamically replaced with the actual table name. |
Prerequisites
-
You have installed Cursor or another tool that supports the MCP protocol (such as Windsurf or Qwen Code).
-
You have deployed seekdb.
- For deployment details, see Deploy seekdb.
-
You have a Python environment set up (version 3.10 to 3.12).
- Download the Python installer from the official Python website.
Procedure
Step 1: Obtain database connection information
Contact the database administrator or deployment team to get the required database connection string. For example:
mysql -h$host -P$port -u$user_name -p$password -D$database_name
Parameters:
$host: The IP address for connecting to seekdb.$port: The port number for connecting to seekdb. Default is2881.$database_name: The name of the database to access.$user_name: The account for connecting to the instance. Default isroot.$password: The account password. Default is empty.
Here is an example:
mysql -hxxx.xxx.xxx.xxx -P2881 -uroot -p****** -Dtest
Step 2: Install Python dependencies
Environment setup
-
Install the uv package manager.
-
On macOS or Linux, run:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh -
On Windows, run:
irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex -
Alternatively, you can install uv using pip:
pip install uv
-
-
Verify the installation:
uv --version
Install OceanBase MCP Server
-
Choose a directory and create a virtual environment:
uv venv -
Activate the virtual environment:
source .venv/bin/activate -
Install OceanBase MCP Server:
uv pip install oceanbase-mcp
Step 3: Configure the MCP Server environment
-
Create a
.envfile with your database connection info:cat > .env <<EOF
OB_HOST=127.0.0.1
OB_PORT=2881
OB_USER=root
OB_PASSWORD=your_password
OB_DATABASE=test
EOF -
Start the MCP Server:
uv run oceanbase_mcp_server \
--transport sse \ # Supports stdio/streamable-http/sse modes
--host 0.0.0.0 \ # Allows external access, use 127.0.0.1 for local access only
--port 8000 # Custom port (update later configs if changed)
Step 4: Connect Cursor to the MCP Server
-
Use Cursor V2.0.64 as an example. Click the Open Settings icon in the upper right corner, select Tools & MCP, and click New MCP Server.

-
Edit the
mcp.jsonconfiguration file:{
"mcpServers": {
"ob-sse": {
"autoApprove": [],
"disabled": false, # Must be set to false to enable the service
"timeout": 60,
"type": "sse",
"url": "http://127.0.0.1:8000/sse" # Make sure this matches the port you set in Step 3
}
}
} -
Verify the connection.
After saving the configuration, return to the Tools & MCP page. Then you will find the newly added MCP server.
-
Once added, Cursor will automatically use MCP tools when you ask questions in the Chat window.

Quick start examples
Once you set up seekdb and the MCP Server, you can quickly try out data analysis capabilities. The following examples use the Online Retail Dataset and Cursor to demonstrate how AI tools can seamlessly work with the OceanBase MCP Server for common analytics tasks.
Customer distribution analysis
-
Instruction input:
Please analyze the customer data and show the distribution of customers by country. -
Cursor execution process:
-
Cursor calls
execute_sqlto run an aggregation query:SELECT Country,
COUNT(DISTINCT CustomerID) AS customer_count
FROM dataanalysis_english.invoice_items
WHERE CustomerID IS NOT NULL
AND Country IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY Country
ORDER BY customer_count DESC; -
Cursor automatically generates a structured analysis result.
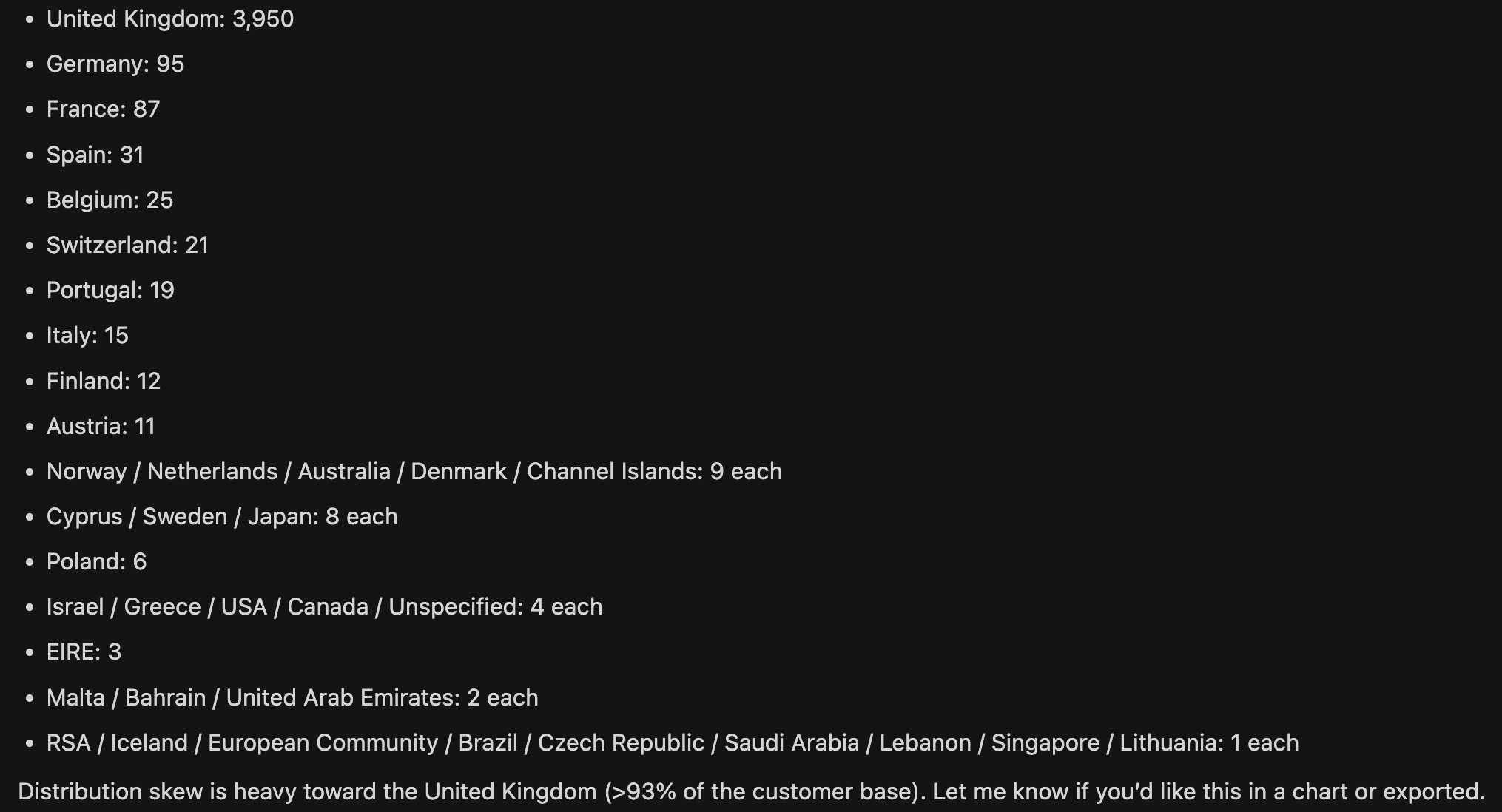
-
-
Further request:
Please convert the above results into a table. -
Output:
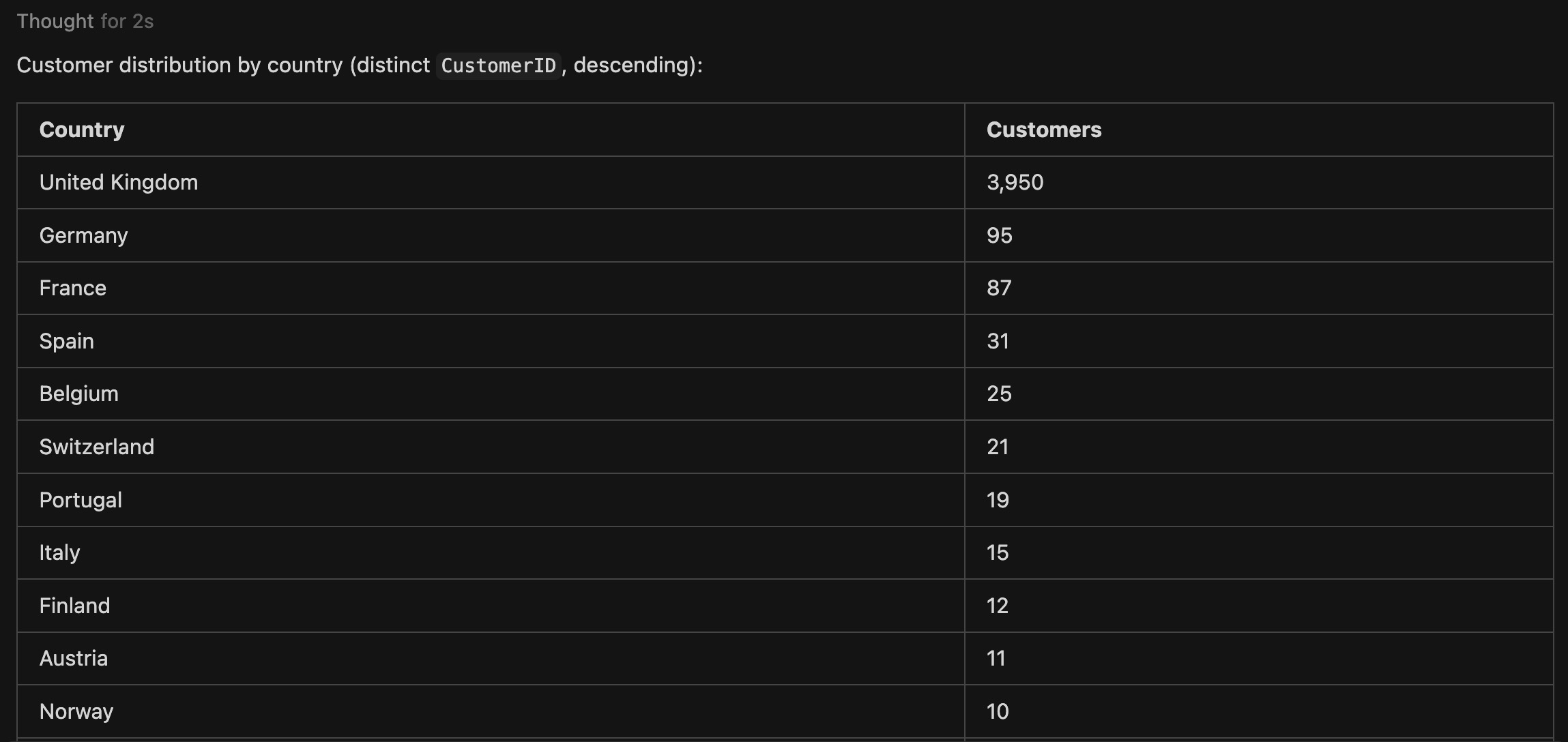
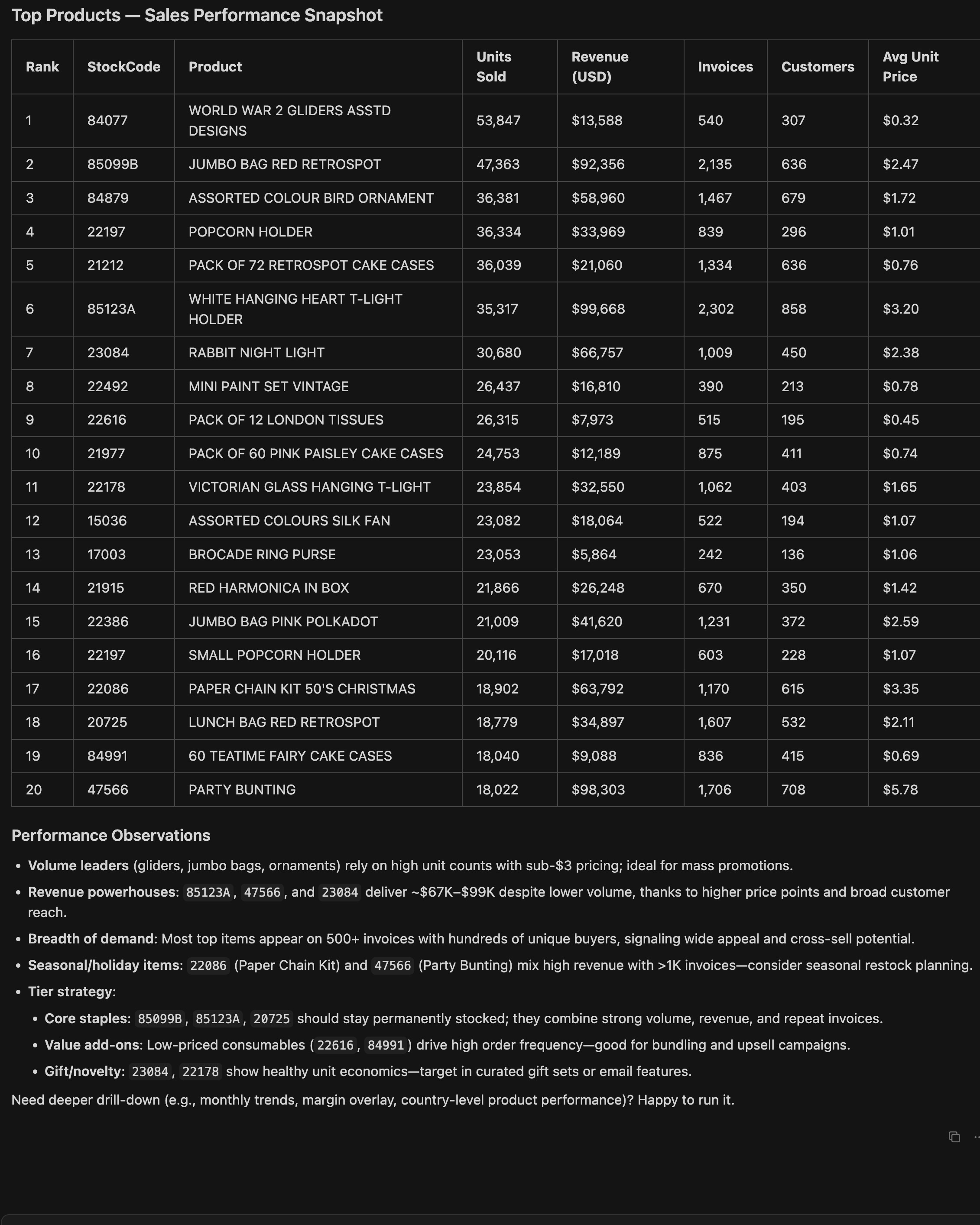
Best-selling products analysis
-
Instruction input:
Find the most popular products and show their sales performance. -
Output:
Cursor summarizes the most popular products with performance insights and displays them in a ranked table or bar chart.
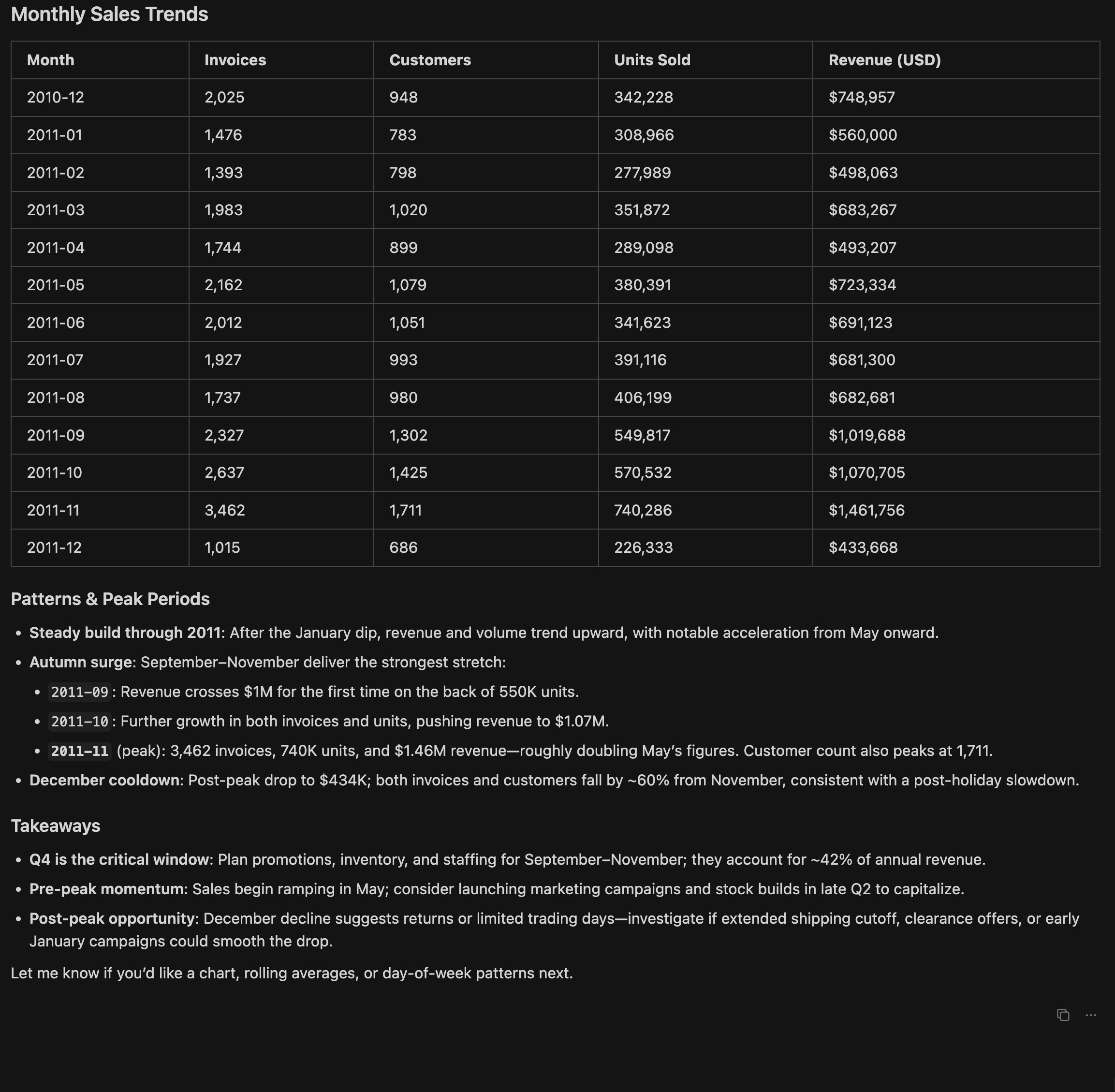
Sales trend over time
-
Instruction input:
Analyze monthly sales trends and identify peak periods. -
Output:
Cursor generates a line chart showing monthly sales trends with peak periods highlighted (for example, November and December for holiday shopping).