SAVEPOINT
Description
This statement is used to create a savepoint within a transaction, allowing for partial rollback of the transaction.
Syntax
-
Creating a savepoint:
SAVEPOINT savepoint_name; -
Rolling back to a savepoint:
ROLLBACK [WORK] TO [SAVEPOINT] savepoint_name; -
Deleting a savepoint:
RELEASE SAVEPOINT savepoint_name;
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| [WORK] | An optional keyword that does not affect the semantics. |
| savepoint_name | The name of the savepoint. The specified savepoint must be unique within the transaction. If a savepoint with the same name already exists, it will overwrite the previous one. After creating a savepoint, you can roll back the transaction to the specified savepoint or use the ROLLBACK statement to roll back the entire transaction. |
Examples
Assume a transaction executes the following statements:
| sql_no | Statement | Partition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | UPDATE ...; | p1, p4 |
| SAVEPOINT sp1; | ||
| 2 | UPDATE ...; | p2, p4 |
| 3 | UPDATE ...; | p3, p5 |
| SAVEPOINT sp2; | ||
| 4 | UPDATE ...; | p1, p3, p6 |
| 5 | UPDATE ...; | p1, p5 |
| SAVEPOINT sp3; | ||
| 6 | SELECT ...; | |
| 7 | UPDATE ...; | p5, p6 |
| SAVEPOINT sp4; |
Record Savepoint
Before committing the transaction, you can create a savepoint. You need to link the savepoints in the order they were created to form a chain. In the above transaction, there are 7 SQL statements and 4 savepoints. The savepoint chain is shown in the following figure, where each node records the mapping between <savepoint_name, sql_no>:

Transaction Participants List
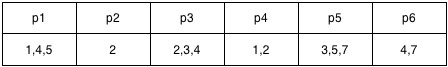
To support rolling back all modifications after a specific SQL statement, the transaction needs to record the participants involved in each statement along with their corresponding sql_no. In the above transaction, 7 SQL statements were executed, involving p1 to p6, a total of 6 partitions:
Savepoint Rollback Process
-
Query the
savepoint_namecorresponding to thesql_nofrom the savepoint chain.For example, if the user executes
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT sp2, the savepoint chain is queried to find thatsp2corresponds tosql_no3. -
Query the partitions corresponding to the
sql_nofrom the transaction participants list.From the transaction participants list, it is found that the partitions involved in statements with
sql_nogreater than 3 arep1,p3,p5, andp6. -
Roll back the partition data based on the partitions identified in step 2. The scheduler initiates a rollback request for these partitions, rolling back all modifications made to the transaction after
sp2.In this case, some modifications on
p1,p3, andp5related to the transaction are rolled back, while all modifications onp6related to the transaction are rolled back. -
Update the transaction participants list.
Modify the transaction participants list to remove the operation information for
sql_nogreater than 3. Since all modifications onp6have been rolled back,p6can be removed from the participants list.
-
Delete invalid savepoints.
After the user successfully executes
ROLLBACK to SAVEPOINT sp2, the system will delete the savepointssp3andsp4, preventing further rollback to those points.